Learn Survival Xhosa
Wikitravel users have collectively created a free Xhosa phrasebook with the goal of making it possible for travelers to "get by" while traveling in areas where Xhosa is spoken.
Wikitravel phrasebooks are available in many languages and each one varies in depth and detail. Most of the phrasebooks include a pronunciation guide, a general phrase list, information about dates and numbers, a color list, transportation-related phrases, vocabulary for shopping and phrases for eating and drinking. Some are even more in depth, and all are free!
From Website
This Xhosa phrasebook is not a language tutorial, comprehensive grammar or dictionary. Its goal is to define just enough of the language so that an English-speaking traveller can "get by" in areas where Xhosa is spoken.
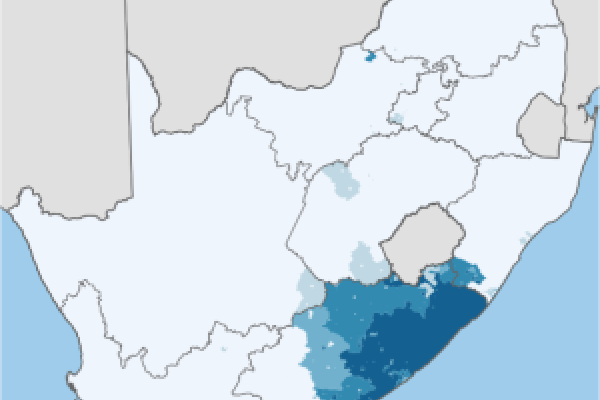
Xhosa (English pronunciation: /ˈkoʊsə/, Xhosa: isiXhosa [isikǁʰóːsa]) is one of the official languages of South Africa. Xhosa is spoken by approximately 7.9 million people, or about 18% of the South African population. Like most Bantu languages, Xhosa is a tonal language, that is, the same sequence of consonants and vowels can have different meanings when said with a rising or falling or high or low intonation. One of the most distinctive features of the language is the prominence of click consonants; the word "Xhosa", the name of the language itself, begins with a click.
Xhosa is the most widely distributed African language in South Africa, while the most widely spoken is Zulu. Xhosa is the second most common home language in South Africa as a whole. As of 2003 the majority of Xhosa speakers, approximately 5.3 million, live in the Eastern Cape, followed by the Western Cape (approximately 2 million), Gauteng (671,045), the Free State (246,192), KwaZulu-Natal (219,826), North West (214,461), Mpumalanga (46,553), the Northern Cape (51,228), and Limpopo (14,225). A minority of Xhosa speakers (18,000) exists in Quthing District, Lesotho.
Xhosa is written using a Latin alphabet-based system.